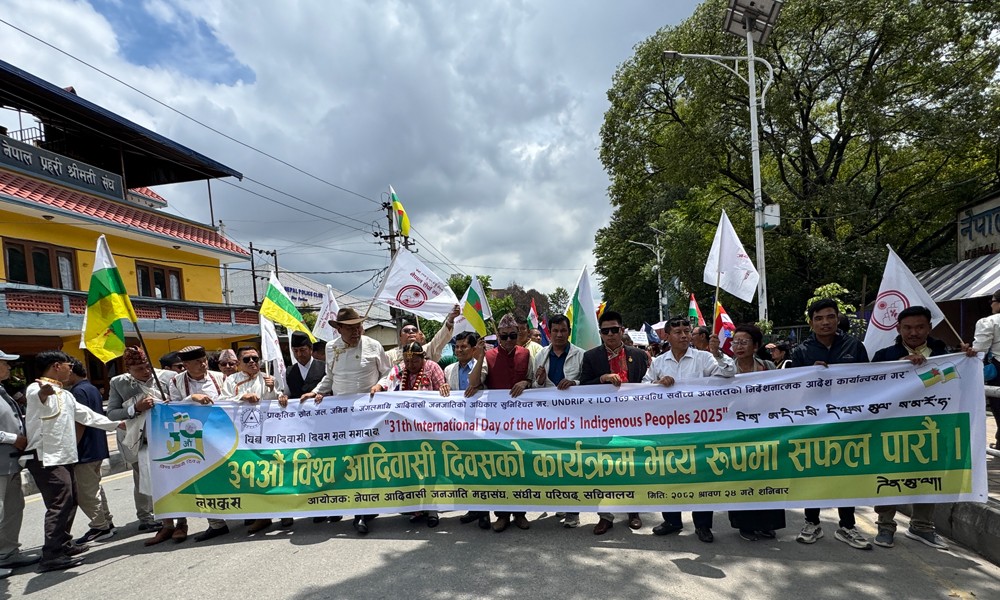
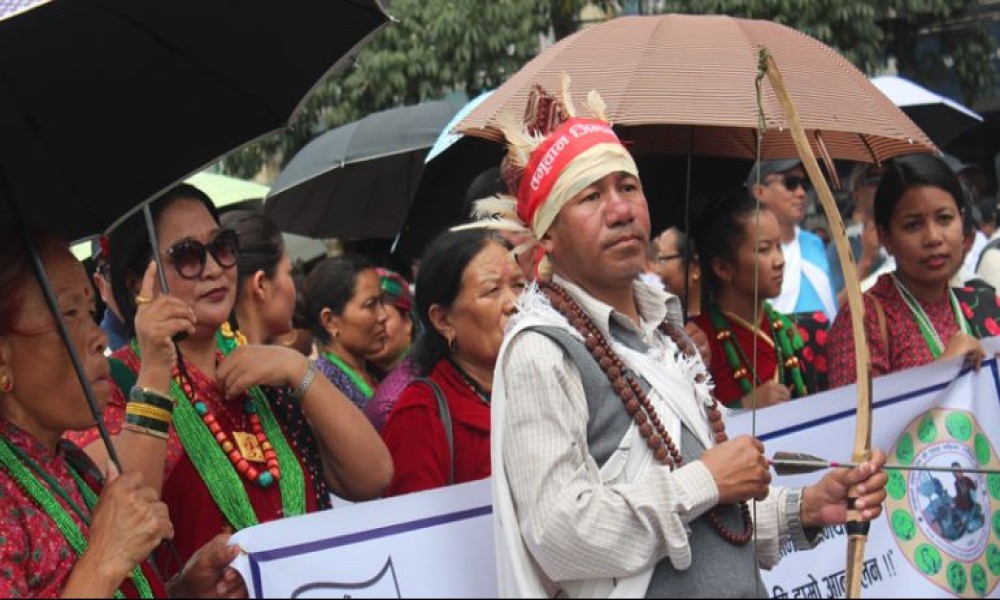
Bhakta Rai
Who are Kiratis? This question has divided researchers and historians. Some say Rais are Kiratis and other indigenous groups are not. Others argue that Kirat is a group of various indigenous groups.
Historian Iman Singh Chemjong says Kirat is a far wider community than it is now made out to be. He argues Gurung, Magar, Thakali, Tamang, Sherpa and other indigenous groups are also Kiratis. Poet and historian Tulasi Diwas says Dhimals are also Kirati. So it is difficult to conclude who are Kiratis and who are not. But broadly speaking, Rai, Limbu, Sunuwar and Yakkha are now believed to be four members of Kirat community.Of these four Kirat sub-groups, I am highlighting several aspects of Kirat Rai in this article.
Historian Iman Singh Chemjong says Kirat is a far wider community than it is now made out to be. He argues Gurung, Magar, Thakali, Tamang, Sherpa and other indigenous groups are also Kiratis
Population and geography
Kirat Rais originally hail from Nepal's eastern hills, but they now can be found in Sunsari, Morang, Jhapa, Udayapur and Kathmandu in significant numbers. As British Gurkha soldiers, Kirat Rais have also reached the UK, Hong Kong, Brunei and other countries. They can also be found in several parts of India, most importantly Sikkim and West Bengal.
Kirat Rai's exact population is unknown because they are scattered beyond Nepal, and most of them use their sub-caste groups like Bantawa, Chamling, Sampang and Kulung to identify themselves. So the figure presented by Nepal's census report about Kirat Rai's population is far less.
Divided into sub-caste groups
People belonging to Kirat Rai community are divided into multiple sub-caste groups. But it is believed that Kirat Rais originally had just 10 sub-caste groups: Athapahare, Bantawa, Chamling, Kulung, Loharung, Mewahang, Nepali, Sampang, Thulung and Chaurasiya. Over the years, sub-caste groups were divided into more sub-caste groups. Today, it is difficult to find out the exact number of sub-caste groups of Kirat Rai.
People belonging to Kirat Rai community are divided into multiple sub-caste groups. But it is believed that Kirat Rais originally had just 10 sub-caste groups:
Even within sub-caste group, Kirat Rais are divided into Pachhas. For example, Kirat Rais belonging to Bantawa sub-caste group have multiple Pachhas like Mangpang, Mukarung, Chhangchha, Isara, etc.
Language
Kirat Rais are rich in language. They have various languages, each sub-caste group boasting of their own Kirat Rai language. But because of the state's one-language policy, migration, inter-caste and inter-sub caste marriages, poverty and influence of other cultures, many Kirat Rai languages have already vanished while others are on the verge of becoming extinct. Bahing, Koyu, Hayu, Yamphu, Yamphe, Chhiling, Loharung and Mehawang languages are fast-disappearing.Of late, various Kirat Rai groups are undertaking efforts to preserve and promote their languages. But it is an uphill task.